The three-axis accelerometer measures acceleration in the X, Y, and Z axes.
When you need to measure acceleration, orientation, or physical movement of the sensor.
This sensor works by housing a Micro Electro-Mechanical System (MEMS) inside of the microchip. Springs suspend floating fingers in between fixed fingers. The floating fingers can move back and forth on one axis. Deflection in one direction or the other causes a change in capacitance between the floating and fixed fingers. This change in capacitance represents acceleration on one axis. There is a system of fingers for all the three axes.
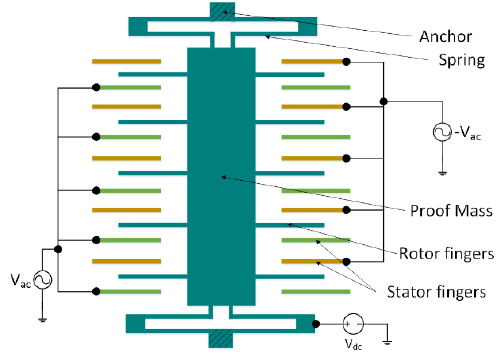
The sensor is very easy to wire; 5 volts to VCC, ground to GND, and feed each of the outputs to one of the analog input lines on the Arduino. All three axes are measured simultaneously. If you only want to use it to measure acceleration in one or two axes, you may simply only wire the ones you want to read.

/*
* This program reads an accelerometer connected to ACCEL_X_PIN,
* ACCEL_Y_PIN, and ACCEL_Z_PIN and sends the data back to the
* computer via serial.
*
* Created 2021-02-19 by Perry Naseck
*/
const int ACCEL_X_PIN = A0; // Analog input pin for X movement
const int ACCEL_Y_PIN = A1; // Analog input pin for Y movement
const int ACCEL_Z_PIN = A2; // Analog input pin for Z movement
// Variables to keep track of the current positions
int accelXPos = 0;
int accelYPos = 0;
int accelZPos = 0;
void setup() {
// Setup serial port to send the accelerometer data back to the computer
Serial.begin(9600);
// Setup the accelerometer inputs
pinMode(ACCEL_X_PIN, INPUT);
pinMode(ACCEL_Y_PIN, INPUT);
pinMode(ACCEL_Z_PIN, INPUT);
}
void loop() {
// Get the current states
accelXPos = analogRead(ACCEL_X_PIN);
accelYPos = analogRead(ACCEL_Y_PIN);
accelZPos = digitalRead(ACCEL_Z_PIN);
// Send the data over serial
Serial.print("X: ");
Serial.print(accelXPos);
Serial.print(" Y: ");
Serial.print(accelYPos);
Serial.print(" Z: ");
Serial.println(accelZPos);
// Delay to not send messages too fast
delay(100);
}